Iterative Project Management: Your Proven Path to Success
- shems sheikh
- May 29, 2025
- 11 min read
Understanding What Makes Iterative Project Management Work
Iterative project management is more than just a popular term. It's a practical way to manage projects that gets real results. Unlike traditional waterfall methods, which follow a strict, step-by-step process, iterative project management focuses on flexibility and adaptation. This is done through repeated cycles, allowing teams to effectively respond to changes and challenges that come up during a project. This means completing projects in smaller, manageable stages, enabling continuous improvement along the way.
The Core Principles of Iterative Project Management
What makes iterative project management different? A few core principles contribute to its success.
Incremental Delivery: Instead of one big launch, iterative projects deliver value in smaller increments. This approach enables early feedback and adjustments, reducing the risk of big problems later. Think of building a house room by room, rather than all at once.
Continuous Feedback: Regular feedback is crucial for iterative projects. This constant communication keeps the project aligned with what stakeholders want and allows adjustments based on real-time information. Feedback can come from clients, users, or even the project team itself.
Collaboration and Communication: Open communication and collaboration between team members and stakeholders are key. This shared understanding creates a more efficient and effective working environment. Tools like Beep can facilitate direct feedback on web projects.
Adaptability: Being able to adapt to change is fundamental to iterative project management. Since plans are revisited and refined at each iteration, teams can easily include new information and adjust as needed.
Iterative project management emphasizes repeated cycles of planning, execution, and evaluation. Its roots go back to the mid-20th century, but it gained prominence with the rise of software development in the 1970s and 1980s. By the 1990s, NASA had adopted iterative methods for software projects. They reported that over 70% of project risks were identified and handled during the early iterations. This drastically improved their overall project outcomes. Explore this topic further here.
Why Choose Iterative Project Management?
Iterative project management offers more than just on-time and within-budget project delivery. It also leads to:
Increased Stakeholder Satisfaction: Involving stakeholders throughout the process and using their feedback increases the likelihood of meeting their expectations.
Reduced Risk: Finding and addressing potential issues early minimizes their impact.
Improved Product Quality: The iterative process allows for continuous improvement and refinement, resulting in a better final product.
Enhanced Team Morale: The collaborative nature and the sense of accomplishment from frequent deliveries can boost team morale and motivation.
These advantages make iterative project management a strong alternative to traditional methods, especially in today's dynamic business environment. By using this flexible and adaptive approach, organizations can improve project outcomes, increase stakeholder satisfaction, and create a more collaborative and efficient work environment. This sets the stage for exploring the measurable impact of iterative project management and the data behind its success.
The Real Numbers Behind Iterative Project Success
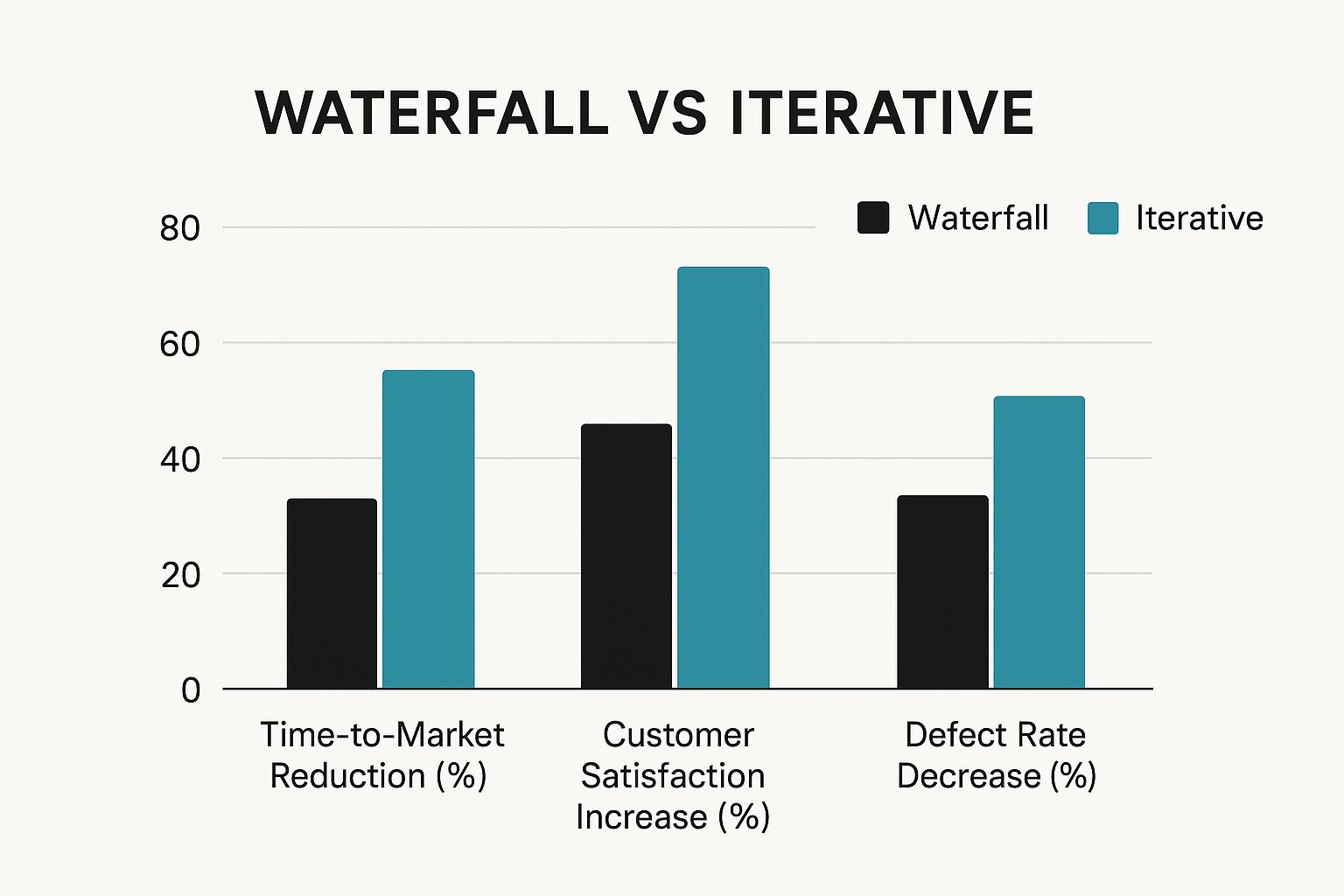
The infographic above provides a clear comparison of Waterfall and Iterative project management across three key areas: Time-to-Market Reduction, Customer Satisfaction Increase, and Defect Rate Decrease. The data tells a compelling story: iterative approaches win on all fronts. They get products out the door faster, make customers happier, and result in fewer bugs. It's no wonder businesses are increasingly embracing iterative frameworks.
This shift towards iterative project management is fueled by the need to be flexible and efficient. Traditional methods often struggle to adapt to evolving needs and market shifts. Imagine designing a car based on last year's trends. By the time it's built, it's already outdated. Iterative project management allows teams to incorporate feedback and adjust throughout the development process. For further insights on stakeholder management, check out this helpful resource: How to master top stakeholder engagement strategies for project success.
Measurable Benefits of Iterative Project Management
One of the strongest arguments for iterative approaches is their impact on project success. This translates into real, tangible benefits. Statistics show that approximately 68% of projects using iterative and Agile frameworks meet their goals, deadlines, and budgets. This is significantly higher than the success rate of traditional methods. By comparison, only about 34% of organizations using traditional project management report on-time and within-budget completion. More detailed statistics can be found here.
This stark contrast underscores the efficiency and effectiveness of iterative methodologies. Beyond just hitting targets, these approaches offer several other key advantages:
Reduced Development Costs: Early issue detection and resolution minimize wasted time and resources.
Faster Time to Market: Incremental value delivery allows for quicker releases, giving businesses a competitive advantage.
Improved Product Quality: Continuous testing and feedback loops lead to better products that truly meet customer needs.
Increased Stakeholder Satisfaction: Regular communication and active involvement keep stakeholders engaged and satisfied.
Let's explore a comparison of success rates between these two project management styles:
The following table illustrates the differences in key performance metrics between iterative and traditional project management.
Iterative vs Traditional Project Management Success Rates
Metric | Iterative Methods | Traditional Methods | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
On-Time and Within Budget Completion | 68% | 34% | 34% |
Customer Satisfaction | High | Moderate | Significant |
Defect Rate | Low | High | Significant |
This table clearly highlights the significant improvements observed with iterative methods, particularly in on-time project delivery and reduced defect rates. This demonstrates the value of adaptability and continuous improvement inherent in these approaches.
Measuring Success: Key Metrics to Track
To get the most out of iterative project management, tracking the right metrics is essential. While traditional methods often fixate on cost and schedule, iterative approaches prioritize value and customer satisfaction.
Here are some key metrics to consider:
Customer Satisfaction Scores: Regularly gather feedback to ensure alignment with customer expectations. Tools like Beep can simplify this process by enabling direct feedback on live websites.
Velocity: Measure the team's work output per iteration to pinpoint bottlenecks and refine planning accuracy.
Defect Rate: Track defects found during testing to gauge product quality and identify areas for improvement.
Business Value Delivered: Evaluate the tangible benefits of each iteration to ensure the project stays aligned with business objectives.
By focusing on these metrics, organizations can gain valuable data insights and make informed decisions to optimize their iterative processes. This data-driven approach not only delivers successful projects but also drives continuous improvement in project management practices.
How Industries Are Embracing Iterative Approaches
Iterative project management isn't just for tech anymore. Its flexible nature is proving incredibly useful across a wide range of sectors, from manufacturing and healthcare to construction and even disaster relief. This growing popularity comes from the need for businesses to be more agile and responsive in today's dynamic markets. For example, manufacturers using iterative approaches can quickly adjust to supply chain disruptions and shifting customer needs.
Adapting Iterative Principles Across Sectors
Every industry has its own unique hurdles, so applying iterative project management requires a tailored approach. This adaptability is a major strength. Understanding capacity planning within project management is key to making iterative projects successful. Jira Capacity Planning offers a deeper look into this important topic.
In healthcare, iterative project management helps teams respond to new regulations or incorporate emerging research while developing medical devices or treatment protocols. Construction companies are also adopting iterative methods to handle unexpected site conditions or material shortages.
The Driving Forces Behind Adoption
The increasing use of iterative project management comes down to its ability to address pain points common across many industries. Traditional project management often struggles with unpredictable factors and changing requirements. This can lead to delays, budget overruns, and ultimately, unmet goals.
The iterative approach, with its emphasis on flexibility and continuous improvement, offers a much better solution. Statistics show that companies using iterative methods report an average project performance rate of 73.8%. Additionally, a PMI survey found that 71% of organizations use Agile methodologies—a type of iterative approach—for at least some of their projects, and this number is constantly growing. For more detailed statistics, check out this resource: Project Management Statistics.
Measurable Impact and Success Stories
The positive impact of iterative project management on businesses is undeniable. Organizations see major improvements in areas like on-time delivery, lower development costs, and higher stakeholder satisfaction.
Let's look at some examples. In software development, iterative methods allow for frequent releases and faster feedback, enabling quicker responses to market demands. In disaster relief, iterative approaches enhance coordination and resource allocation, leading to more effective responses. And in manufacturing, iterations optimize production processes and product quality, ultimately boosting customer satisfaction. These success stories clearly demonstrate the value of iterative project management across a variety of sectors.
Choosing The Right Framework For Your Team
Finding the perfect project management approach isn't a one-size-fits-all endeavor. The real key is selecting a framework that works best for your team and the specific project. This involves carefully considering popular options like Scrum, Kanban, and hybrid approaches, weighing their pros and cons within your organization's context. Making the right choice can heavily influence your project's success.
Exploring Popular Iterative Frameworks
Each framework offers a unique way to handle iterative project management. Scrum, known for its structured approach, uses defined roles, events (like daily stand-ups and sprint reviews), and artifacts (like the product backlog and sprint backlog). This structure makes it ideal for complex projects needing regular communication and close collaboration. For remote teams, adapting project management strategies is crucial; learn more about effective remote project management from this helpful resource: How to master project management for remote teams.
Kanban offers a different, more flexible, flow-based system. It visually represents the workflow, limits work in progress, and prioritizes continuous delivery. This makes it a good fit for projects with changing requirements and a need to quickly adapt.
Hybrid approaches offer the best of both worlds, combining elements from different frameworks. This gives teams the freedom to choose practices that best suit their specific needs, especially beneficial for unique project circumstances.
Matching Framework to Project and Team
Picking the right framework depends on several factors, like project complexity, team size, and company culture. For involved projects with numerous dependencies, Scrum's organized nature provides essential control and transparency. Smaller, simpler projects might benefit more from Kanban's flexibility.
Team experience also matters. Teams just starting with iterative approaches might find Scrum's structured guidance helpful. More seasoned teams might appreciate Kanban's autonomy and focus on continuous improvement.
To help you choose, the following table compares popular iterative project management frameworks, highlighting their key features, ideal use cases, and how complex they are to implement:
To help you select the best fit for your team, the table below compares some popular iterative project management frameworks:
"Popular Iterative Project Management Frameworks"
Framework | Key Features | Best For | Team Size | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Scrum | Sprints, defined roles, ceremonies | Complex projects, frequent releases | Small to medium | Moderate |
Kanban | Visual workflow, work-in-progress limits, continuous flow | Evolving requirements, rapid response | Small to large | Low |
Hybrid | Combination of different practices | Tailored to specific needs | Varies | Varies |
This table offers a quick overview to help guide your decision-making process when selecting an iterative framework.
Avoiding Common Implementation Pitfalls
While iterative project management offers numerous advantages, it’s important to be mindful of potential issues. Lack of management buy-in, insufficient training, and resistance to change can hinder even the most well-planned projects. Clearly defined roles, thorough training, and open communication can help address these obstacles.
Another common mistake is rigidly adopting a framework without tailoring it to the project's and team's unique needs. The goal is to choose the practices that best suit your specific situation, not to force-fit a pre-determined methodology. By carefully considering your options and making smart choices, you can fully leverage the power of iterative project management for project success.
Making The Transition Without Breaking Everything

Implementing iterative project management requires a thoughtful approach. It's not just about deciding to make a change; it's about meticulously planning how you'll get there. This encompasses everything from choosing the right initial projects to expanding these practices across your teams. This section will walk you through the key steps for smoothly integrating iterative project management into your organization.
Strategic Planning For A Smooth Transition
Successful transitions begin with a solid plan. This means identifying suitable pilot projects. Start with projects that are well-defined, yet offer room for flexibility. This creates a learning environment where adjustments can be made safely. Choosing the right framework is also essential, and understanding the various approaches available is key, as discussed in this guide to Scrum Meetings.
Establish clear goals and metrics for these pilot projects. This helps measure the impact of the iterative approach and showcase its effectiveness to stakeholders. Using data to demonstrate success makes the transition easier and builds support within the organization.
Managing Change and Building Buy-In
Change can be difficult. Resistance is expected, so it's important to address concerns proactively and offer comprehensive training. This empowers your teams to adopt new methodologies with confidence.
Getting stakeholders on board is vital. Clearly communicate the advantages of iterative project management and show how it aligns with overall business objectives. Highlighting positive results from pilot projects can significantly influence stakeholders and gain their support.
Adapting Existing Processes and Workflows
Transitioning to iterative project management doesn't mean throwing out your current processes. Instead, identify which elements align with iterative principles and incorporate them into your new approach.
This enables a more gradual shift, minimizing disruption. For example, you could start by incorporating regular feedback loops and delivering work in increments on existing projects. This can be a stepping stone before fully adopting a specific framework. You might also find this resource helpful: How to master backlog grooming best practices.
Measuring Progress and Ensuring Continuous Improvement
Clear metrics for progress are essential. Track key performance indicators (KPIs), like project velocity, client satisfaction, and error rates. This gives you valuable data on how the iterative approach is impacting projects.
Integrate feedback loops into your workflow. Regularly solicit feedback from team members, stakeholders, and clients to identify areas for improvement. This continuous evaluation ensures your iterative project management approach remains adaptable and effective. Addressing typical implementation challenges, like resistance to change or unclear communication, is crucial for maximizing the benefits. By following these practical steps, you can ensure a smooth transition and unlock the true potential of the iterative approach.
Building Systems That Drive Continuous Improvement
Effective iterative project management isn't just about ticking boxes and finishing tasks. It's about constantly evaluating and refining the way you work, understanding the impact of your deliverables on the business, and analyzing how your team functions as a whole. This section explores building Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that truly matter, establishing effective feedback systems, and crafting insightful reports that offer actionable advice—going beyond superficial numbers.
Measuring What Matters: Beyond Completion Rates
While tracking completed tasks is important, successful iterative project management focuses on the bigger picture. It's about measuring the genuine value delivered to the business. For instance, if you're launching a new website feature, don't just track its on-time release. Analyze its impact on user engagement and conversion rates. This broader perspective helps ensure every iteration contributes meaningfully to overall project objectives.
Team performance metrics should also delve deeper than simple productivity. Consider qualitative measures like team morale, communication effectiveness, and adaptability. These offer valuable insights into team dynamics and highlight potential areas for improvement. This holistic view fosters a positive and productive team environment, contributing significantly to project success.
Establishing Meaningful KPIs
Choosing the right KPIs is essential for driving tangible progress. These KPIs should be directly tied to the project's goals and readily measurable. If your project aims to boost customer satisfaction, the Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a relevant KPI. It quantifies how likely customers are to recommend your product or service.
Setting realistic KPI targets is crucial. This prevents unrealistic expectations and ensures the KPIs genuinely motivate the team. Instead of aiming for an immediate, drastic NPS increase, set incremental, achievable milestones. This encourages continuous improvement and fosters a sense of accomplishment along the way.
Implementing Effective Feedback Loops
Feedback loops are vital for iterative project management, enabling teams to learn from each cycle and adjust their approach accordingly. Gather feedback from diverse sources, including stakeholders, customers, and the team itself. Tools like Beep facilitate direct feedback on web projects, allowing users to comment directly on live pages.
Gathering feedback is just the first step. Acting upon it is equally crucial. This shows stakeholders and customers that their input is valued, encouraging continued engagement. This closed-loop approach fosters a culture of continuous improvement and keeps the project aligned with its objectives.
Building Reporting Systems for Actionable Insights
Reporting systems should go beyond visually appealing charts and graphs. They should provide clear, actionable insights to inform future iterations. Present data in an easy-to-understand format, highlighting key trends and patterns.
Focus on the "why" behind the data, not just the numbers themselves. If a KPI isn't meeting its target, the report should offer potential explanations and suggest solutions. This transforms the reporting system from a passive record-keeping tool into an active driver of continuous improvement.
The Power of Retrospectives
High-performing teams use retrospectives to review past iterations and identify areas for improvement. These meetings create a safe space for open discussions about successes, challenges, and potential process refinements.
Retrospectives are a potent tool for continuous improvement. They facilitate learning from mistakes, celebrating achievements, and adapting processes. This regular reflection ensures long-term success and helps teams navigate evolving business needs while maintaining high morale and productivity. By embracing these strategies, organizations can build iterative project management systems that promote continuous learning, adaptation, and ultimately, successful project outcomes.
Ready to streamline your feedback and collaboration? Start your free trial of Beep today and revolutionize how your team reviews web projects.

.png)
Comments