Top 10 User Testing Methods to Refine Your UX in 2025
- shems sheikh
- Dec 26, 2025
- 16 min read
In the competitive digital landscape, guessing what users want is a recipe for failure. The most successful products are built on a deep, empathetic understanding of user behavior, needs, and motivations. But how do you bridge the gap between your assumptions and their reality? The answer lies in a robust testing strategy that directly involves your target audience. This is more than just a box-ticking exercise; it's a foundational process for creating intuitive, engaging, and valuable experiences.
This guide moves beyond theory to provide a practical roundup of the 10 most effective user testing methods used by leading product teams. From the in-depth qualitative insights of moderated sessions to the scalable quantitative data from A/B tests, we'll explore the tools, techniques, and best practices for each approach. Implementing these robust user testing methods is fundamental for developing effective UX strategies in website design, ensuring your product truly connects with its audience.
By the end of this article, you won't just know what these methods are; you'll have a complete toolkit to gather actionable feedback, eliminate guesswork, and confidently build products that resonate. We'll dive straight into the specifics, covering everything from moderated usability testing and contextual inquiry to heatmap analysis and card sorting.
1. Moderated Usability Testing
Moderated usability testing is a foundational user testing method where a facilitator guides a participant through specific tasks in real time. This direct interaction, either in person or remote, allows the moderator to ask follow-up questions, probe deeper into user behavior, and clarify confusion on the spot. It is invaluable for understanding the "why" behind user actions, not just the "what."
This method excels at uncovering complex usability issues and gathering rich, qualitative data. For instance, Adobe uses moderated sessions to get nuanced feedback on new interface features, observing designers' initial reactions and thought processes as they navigate unfamiliar tools.

Best Practices for Moderated Testing
To get the most out of your sessions, focus on creating a structured yet flexible environment. The goal is to observe natural behavior while ensuring you cover key research questions.
Create Realistic Scenarios: Instead of giving direct commands, frame tasks as real-world goals. For example, say "Imagine you need to share this design with your team for feedback," not "Click the share button."
Focus on Core Tasks: Limit each session to 3-5 essential tasks to avoid participant fatigue and keep the feedback concentrated on your highest priorities.
Document and Share: Use tools like Beep to capture live feedback with visual annotations directly on your website or prototype. Recording sessions and sharing key moments via Slack integrations keeps the entire team aligned.
Observe Emotions: Pay attention to non-verbal cues like sighs, pauses, or expressions of delight. These often reveal more about the user experience than words alone.
Pioneered by usability experts like the Nielsen Norman Group, this approach is highly effective. The key is in the preparation and active listening during the session. To dive deeper into the process, you can explore a comprehensive guide on how to conduct effective usability testing.
2. Unmoderated Remote Testing
Unmoderated remote testing is a user testing method where participants complete tasks independently in their own environment, without a facilitator present. This asynchronous approach uses specialized platforms to record a user's screen, clicks, and verbal feedback as they think aloud. It’s ideal for gathering data at scale and testing with a geographically dispersed audience.
This method excels at collecting quantitative metrics alongside qualitative insights efficiently. For example, enterprise clients on UserTesting.com deploy unmoderated tests to validate design changes with hundreds of users simultaneously, gathering rapid feedback on prototypes before development begins. This approach makes it a staple for many modern product teams.
Best Practices for Unmoderated Testing
Since there's no facilitator to clarify instructions, the success of unmoderated testing hinges on crystal-clear preparation. The goal is to create a seamless, self-guided experience for participants.
Write Flawless Task Descriptions: Your instructions must be unambiguous. Instead of "Find our new feature," say "Imagine you want to create a project report. Show me how you would do that starting from the dashboard."
Keep Sessions Short: Aim for sessions that are 15-20 minutes long. This maintains participant engagement and leads to higher completion rates and more thoughtful feedback.
Screen Your Participants: Use screener questions to ensure every participant accurately represents your target user profile, guaranteeing the relevance and quality of your data.
Capture Visual Context: Use a tool like Beep to let remote testers provide asynchronous feedback with visual annotations. This adds a crucial layer of context to their recorded actions and verbal comments.
Pioneered by platforms like UserTesting and TryMyUI, this method offers unparalleled speed and scale. By automating the data collection, teams can focus their energy on analysis. For a closer look at asynchronous feedback tools, you can explore how to get user feedback with a Chrome extension.
3. A/B Testing (Split Testing)
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a controlled experimental method where two or more versions of a webpage or feature are shown to similar users simultaneously. By tracking metrics like click-through and conversion rates, this quantitative approach provides data-backed evidence to determine which version performs better. It is exceptionally valuable for making data-driven decisions and optimizing specific user interactions with scientific precision.
This method excels at validating hypotheses and making incremental improvements that significantly impact business goals. For example, Amazon constantly tests different product page layouts to optimize sales, while SaaS companies use it to improve checkout flow conversion rates. It removes guesswork, ensuring design changes are based on actual user behavior.
Best Practices for A/B Testing
To ensure your A/B testing results are reliable and actionable, focus on methodical execution and clear analysis. The goal is to isolate variables and gather statistically significant data.
Test One Variable at a Time: To clearly attribute performance changes, modify only a single element between versions, such as a headline, button color, or image.
Define Success Metrics First: Before launching a test, decide what you will measure. Whether it's sign-ups, downloads, or time on page, a predefined goal is crucial.
Run Tests for Full Business Cycles: Let tests run long enough to account for variations in user behavior, such as weekday versus weekend traffic. A week is often a minimum.
Analyze Qualitative Feedback: After a winning variant is declared, use a tool like Beep to gather visual feedback on why it performed better. Understanding the user's reasoning adds crucial context to your quantitative data.
Pioneered at a large scale by companies like Google, this is one of the most effective user testing methods for optimization. The key is combining rigorous statistical analysis with a deep curiosity about user motivations.
4. Eye Tracking
Eye tracking is a biometric user testing method that provides objective data on where users look on a screen. Using specialized equipment, it measures gaze points, fixation duration, and the path of a user's visual attention. This powerful technique reveals subconscious behavior, showing what truly captures a user's attention and what gets ignored, often uncovering insights that participants themselves cannot articulate.
This method is exceptional for optimizing visual hierarchy and interface layouts. For example, e-commerce sites use eye tracking to test product page designs, ensuring customers see key information like price and add-to-cart buttons. Similarly, Google has famously used gaze pattern data to refine the layout of its search results pages, maximizing ad visibility and user efficiency.
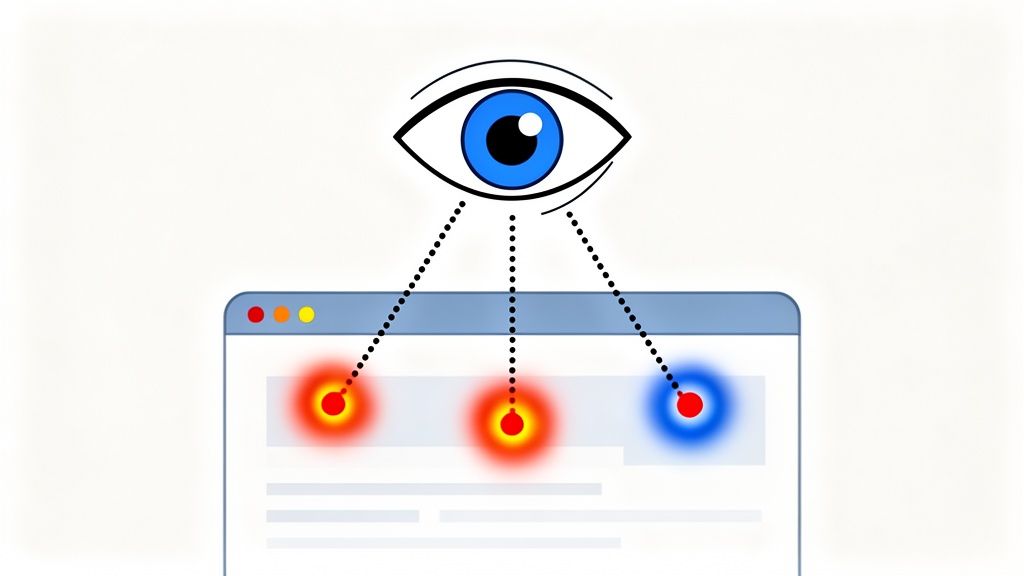
Best Practices for Eye Tracking
To generate reliable data, eye tracking studies require careful setup and interpretation. The goal is to correlate visual attention with user intent and task success.
Combine with Qualitative Methods: Pair eye tracking with a moderated "think-aloud" protocol. While eye tracking shows what users see, asking questions reveals why they look there.
Use Heat Maps for Validation: Analyze heat maps and gaze plots to validate your information architecture. These visualizations quickly show if users are focusing on the intended primary elements.
Ensure Proper Calibration: Calibrate the eye tracking equipment for each participant before the session begins. Accurate calibration is critical for collecting valid gaze data.
Correlate Gaze with Success: Don't just analyze where users look; connect that data to task completion rates. A high-attention area that leads to confusion is a clear red flag.
Pioneered by research from firms like the Nielsen Norman Group and technology from companies like Tobii Pro, eye tracking offers an unparalleled window into the user's visual experience. When used correctly, it provides a scientific foundation for design decisions.
5. Heatmap Analysis
Heatmap analysis is a powerful user testing method that provides a visual representation of how users interact with a webpage. By using color gradients, typically with red indicating high activity and blue showing low activity, heatmaps illustrate where users click, scroll, and move their cursors. This passive data collection technique offers quantitative insights into actual user behavior at a large scale without requiring direct participant interaction.
This method excels at identifying patterns and revealing unexpected user behaviors. For instance, an e-commerce site might use a scroll map to discover that most users never see important product filters placed below the fold. Similarly, SaaS platforms like Hotjar or Microsoft Clarity often use click maps to identify "rage clicks" on non-interactive elements, signaling user frustration and confusion.
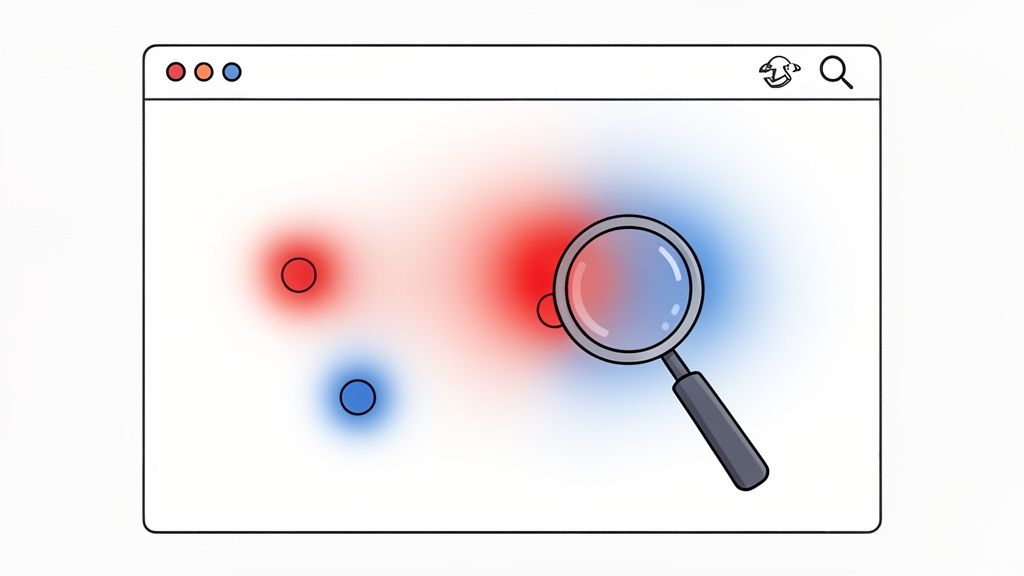
Best Practices for Heatmap Analysis
To extract meaningful insights, you need to go beyond simply viewing the colorful visualizations. Contextualizing the data is key to making informed design decisions.
Segment Your Data: Analyze heatmaps based on different user segments, such as new vs. returning visitors or traffic source (e.g., organic search vs. social media). This helps uncover distinct behavior patterns.
Prioritize Rage Clicks: Clicks on non-clickable elements often indicate significant usability problems. Treat these as high-priority issues to investigate and fix.
Optimize Content Placement: Use scroll maps to determine how far down the page most users go. Place your most critical calls-to-action and information above this fold line.
Combine with Qualitative Feedback: Heatmaps show you what users are doing, but not why. Use tools like Beep to layer qualitative feedback directly onto heatmap screenshots, allowing your team to discuss specific findings and propose solutions.
Popularized by tools like Crazy Egg and Hotjar, heatmap analysis is a cornerstone of modern conversion rate optimization. When combined with other user testing methods, it provides a comprehensive picture of the user experience.
6. User Interviews
User interviews are in-depth, one-on-one conversations designed to explore a user's motivations, needs, and pain points. Unlike task-based testing, this method is open-ended and exploratory, allowing researchers to understand the broader context of a user's world, their mental models, and their overarching goals. It's a foundational qualitative research practice for uncovering deep insights.
This user testing method is essential for foundational research and building empathy. For example, the team behind Slack conducted extensive interviews with power users to understand exactly how they integrated the tool into complex team workflows, which directly informed feature development. Similarly, early interviews at Figma helped uncover designers' frustrations with traditional, non-collaborative tools.
Best Practices for User Interviews
To conduct effective interviews, your focus should be on creating a comfortable, conversational atmosphere where the participant feels empowered to share openly. The goal is to listen more than you talk and guide the conversation toward your research objectives without leading the user.
Prepare a Guide, Not a Script: Create an interview guide with key questions and topics, but be prepared to deviate. Follow interesting threads and ask spontaneous follow-up questions to dig deeper.
Ask "Why" Repeatedly: When a user shares an opinion or behavior, gently ask "why" several times. This technique, known as the "5 Whys," helps you move past surface-level answers to uncover core motivations.
Recruit Real Users: Avoid convenience samples. Recruit participants who accurately represent your target audience to ensure the insights are relevant and actionable for your product.
Share Compelling Clips: Record interviews (with permission) and share short, impactful video clips with your team. Hearing feedback directly from users is a powerful way to build empathy and drive alignment.
Popularized by experts like Erika Hall in Just Enough Research, this approach is invaluable for discovery. The key is preparing thoughtful questions and practicing active, empathetic listening to truly understand the person behind the screen.
7. Card Sorting
Card sorting is a powerful user testing method that reveals how people understand and group information. In this participatory research technique, users are asked to organize topics (often written on cards) into categories that make sense to them. This process is essential for designing an intuitive information architecture, as it directly taps into your users' mental models.
This method is particularly effective for structuring website navigation, organizing product categories, or designing the layout of a help center. For instance, an e-commerce site might use card sorting to determine whether "Running Shoes" should be categorized under "Footwear," "Sports," or "Men's/Women's," based entirely on user logic.
Best Practices for Card Sorting
Effective card sorting sessions provide a clear blueprint for your content structure. The goal is to uncover patterns in how different users perceive and relate your content.
Start with Open Sorts: In an open sort, participants group cards into categories and then name the categories themselves. This is ideal for discovering your users' natural vocabulary and classification schemes.
Use Closed Sorts for Validation: In a closed sort, you provide predefined categories, and participants assign cards to them. This is useful for validating an existing or proposed structure.
Aim for Statistical Confidence: To get reliable quantitative data, aim to conduct sessions with 20-30 participants. This provides a solid foundation for identifying common patterns.
Analyze Groupings and Labels: Use tools like OptimalSort to generate dendrograms and similarity matrices. These visualizations make it easy to spot consensus on how items are grouped together.
Popularized by experts like Donna Spencer, this approach builds a user-centric foundation for your design. By understanding how users think, you can create navigation and content structures that feel effortless. For a closer look at analysis, you can explore Optimal Workshop’s guide on analyzing card sorting results.
8. Contextual Inquiry
Contextual inquiry is an ethnographic research method where researchers observe and interview users in their natural environment as they perform authentic tasks. This immersive approach combines real-time observation with in-context questions to understand users' actual workflows, tools, and pain points that might not surface in a lab setting. It is invaluable for uncovering tacit knowledge and contextual factors influencing user behavior.
This method excels at revealing deep, nuanced insights into how products fit into users' real lives. For instance, a healthcare software company might use contextual inquiry to observe clinicians during their rounds, uncovering workflow inefficiencies that would never be mentioned in a formal interview. This type of deep dive is a core part of many qualitative user testing methods.
Best Practices for Contextual Inquiry
To conduct a successful contextual inquiry, the focus is on observing natural behavior and understanding the user's world with minimal disruption. The researcher acts as an apprentice, learning from the user, who is the expert.
Observe Without Interrupting: The primary goal is to see real behavior. Hold non-critical questions until a natural pause in the workflow to avoid altering their process.
Ask Probing Questions In-Context: When a user performs a specific action or expresses frustration, ask questions like, "Can you tell me why you did that?" or "What were you thinking there?"
Document the Environment: Take photos or videos (with permission) of the user's workspace, tools, and any physical workarounds they use. This context is often as important as the digital interaction itself.
Synthesize and Share Findings: After several sessions, synthesize observations to identify patterns and themes. Share these rich, story-driven insights with the broader team to build empathy and inform design decisions.
Pioneered by Hugh Beyer and Karen Holtzblatt, this method provides a foundational understanding of user needs, which complements other evaluative techniques. To learn more about assessing usability based on established principles, explore this practical guide to heuristic evaluation.
9. Think-Aloud Protocol
The Think-Aloud Protocol is a powerful qualitative user testing method where participants continuously verbalize their thoughts as they interact with a product. By speaking their internal monologue aloud, users reveal their expectations, frustrations, and decision-making processes in real time. This raw, unfiltered feedback provides a direct window into the user's mental model, helping teams understand the reasoning behind their actions.
This technique is exceptionally effective for identifying points of confusion in a user journey. For instance, a software company can use it to evaluate a new onboarding flow, listening as a user explains what they think a button does before clicking it, revealing discrepancies between the design's intent and the user's perception.
Best Practices for Think-Aloud Protocol
The success of this method hinges on making the participant comfortable with verbalizing their thought process. A well-prepared session can yield incredibly detailed insights into user cognition.
Practice with Participants: Start with a simple, unrelated task (e.g., "Tell me your thoughts as you find the weather in another city") to help users get used to speaking aloud.
Use Gentle Prompts: If a participant falls silent, use non-leading prompts like, "What are you thinking now?" or "What are you looking at?" to encourage them to continue verbalizing.
Record and Transcribe: Always record audio and video to capture the full context. Transcription services can help manage the extensive data and make analysis more efficient.
Create Highlight Reels: Share short video clips of key "aha" moments or points of major confusion with stakeholders. This makes the user's struggle tangible and memorable for the entire team.
Popularized by usability pioneers like the Nielsen Norman Group, this method is a cornerstone of qualitative research. When combined with tools like Beep, which capture visual context alongside feedback, the insights become even more actionable for development and design teams.
10. Usability Testing with Live Feedback Annotation (Beep Integration)
This modern user testing method enhances traditional usability testing by integrating real-time visual annotation directly onto live websites or prototypes. As participants navigate the product, observers can add comments, highlight issues, and provide feedback directly on the page. Each annotation automatically captures a screenshot and associated metadata, creating a rich, contextual record of the session.
This approach bridges the gap between moderated observation and asynchronous team collaboration. For instance, a remote marketing team can gather client feedback on a live campaign page across different time zones, with each comment pinpointed to the exact visual element in question. This eliminates ambiguity and streamlines the revision process.
Best Practices for Live Annotation
To maximize the value of live annotation, focus on creating clear, actionable feedback that the entire team can understand and act upon without needing to re-watch entire session recordings.
Be Specific in Annotations: Instead of vague notes like "this is confusing," write specific feedback such as "User hesitated here; consider renaming the 'Submit' button to 'Create Account'."
Use a Priority System: Assign priority colors or labels to comments (e.g., red for critical bugs, yellow for UI suggestions) to help teams quickly identify and address the most important issues first.
Integrate with Your Workflow: Use tools like Beep to send annotated feedback directly to Slack for immediate team alignment or export issues to a Jira board to seamlessly integrate with development sprints.
Combine with Think-Aloud: Encourage participants to verbalize their thoughts while you annotate. This combines qualitative "why" insights with the visual "where" of the issue, creating a comprehensive feedback loop.
Pioneered by visual feedback platforms like Beep, this method is especially powerful for distributed teams. It provides a shared visual space for feedback, making it one of the most efficient user testing methods for modern product development. To explore the technology enabling this approach, you can compare some of the best website annotation tools.
Comparison of 10 User Testing Methods
Method | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes ⭐📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Moderated Usability Testing | 🔄 High — facilitator-led sessions, scripting and moderation skills required | ⚡ Moderate — small participant panels, recording tools, skilled moderators | Deep qualitative insights; explains why users behave a certain way | Complex flows, concept validation, empathy-building workshops | Direct probing, adaptable follow-ups, rich behavioral data |
Unmoderated Remote Testing | 🔄 Low–Medium — create clear tasks on a platform, no live facilitator | ⚡ Low — platform subscription, broad participant recruitment | Scalable quantitative + recorded qualitative clips; natural-context behavior | Large-scale validation, distributed users, fast iteration cycles | Fast collection at scale; removes moderator bias; cost-efficient |
A/B Testing (Split Testing) | 🔄 Medium — experiment setup, tracking, and statistical control | ⚡ Medium–High — analytics, dev support, sufficient traffic | Quantitative performance comparisons; conversion and engagement metrics | Conversion optimization, incremental UI changes, feature impact measurement | Clear, statistically-backed decisions; minimizes subjective debates |
Eye Tracking | 🔄 High — controlled lab setup and calibration; specialized protocols | ⚡ High — eye-tracking hardware/software and trained analysts | Objective gaze data (heatmaps, gaze paths); attention and scan patterns | Visual hierarchy testing, ads, critical information placement | Precise measurement of visual attention; reveals overlooked elements |
Heatmap Analysis | 🔄 Low — deploy tracking script and review visual reports | ⚡ Low — analytics tool and sufficient site traffic | Interaction heatmaps (clicks, scrolls, mouse); identifies hot/dead zones | Identifying UX friction, content placement, ongoing monitoring | Passive, continuous behavioral data at scale; quick diagnostics |
User Interviews | 🔄 Medium — interview guides, recruitment, skilled interviewer | ⚡ Medium — time per participant, recording and transcription | Deep contextual insights into motivations, needs, and pains | Discovery research, strategic product decisions, empathy building | Uncovers unmet needs and long-term user context; rich narratives |
Card Sorting | 🔄 Low–Medium — prepare items and decide open/closed approach | ⚡ Low — cards or digital tool and participant groups | Data-driven groupings and taxonomy suggestions; consensus patterns | Information architecture, navigation, labeling decisions | Reveals users' mental models; quick and quantifiable IA input |
Contextual Inquiry | 🔄 High — in-situ observation and concurrent questioning | ⚡ High — travel/time, access to environments, skilled researchers | Rich workflow and contextual insights; uncovers tacit practices | Complex enterprise workflows, B2B tools, real-world task observation | Reveals real behavior, workarounds, and environmental constraints |
Think-Aloud Protocol | 🔄 Medium — coach participants to verbalize during tasks | ⚡ Low–Medium — recording, transcription and analysis time | Direct insight into user reasoning, expectations, and confusion | Concept clarity, complex tasks, understanding mental models | Exposes decision process in real time; identifies cognitive mismatches |
Usability Testing with Live Feedback Annotation (Beep) | 🔄 Medium — integrate annotation tooling and plan live tests | ⚡ Medium — Beep platform, live site access, team training | Visual, location-specific feedback with screenshots and comments | Remote collaboration, rapid iteration, distributed product teams | Visual clarity of issues, seamless workflow integrations, faster actioning |
From Insight to Impact: Choosing the Right Testing Method
Having a comprehensive list of user testing methods at your disposal is like a craftsperson having a full toolbox. The real skill lies not just in knowing what each tool does, but in selecting the perfect one for the specific task at hand. The journey from raw user insight to tangible product impact is paved with strategic decisions about which method to deploy, when, and why. There is no single "best" method; instead, the optimal approach is always contextual, a tailored response to your unique research questions.
Your choice of user testing methods will be shaped by a few critical factors: your research goals, your timeline, your budget, and your current stage in the product development lifecycle. The methods we've explored are not mutually exclusive but are powerful components of a holistic user research strategy. By understanding their distinct strengths, you can build a robust framework for continuous learning and improvement.
Matching the Method to Your Mission
To translate theory into practice, think of your product development as a journey with distinct phases, each benefiting from specific user testing methods:
For Early-Stage Discovery & Exploration: When you're still defining the problem and exploring user needs, qualitative methods are your best friends. User Interviews and Contextual Inquiry provide the deep, foundational understanding you need to build with empathy. These methods uncover the "why" behind user behaviors.
For Design Validation & Information Architecture: As you move from ideas to wireframes and prototypes, you need to validate your design direction. Moderated Usability Testing offers direct, interactive feedback, while Card Sorting helps ensure your information architecture is intuitive and aligns with user mental models.
For Optimization & Performance Measurement: Once your product is live, the focus shifts to refinement and data-driven growth. Quantitative user testing methods like A/B Testing and Heatmap Analysis provide clear, statistical evidence to optimize conversion rates, engagement, and overall performance.
For Capturing Unfiltered Thoughts: To get a direct line into your user's thought process as they navigate your product, the Think-Aloud Protocol remains an invaluable and straightforward technique. It's a versatile method that can be applied during moderated or unmoderated sessions to reveal moments of confusion or delight.
The Power of a Hybrid Approach
The most successful teams don't just pick one method and stick with it. They create a powerful feedback loop by strategically combining qualitative and quantitative approaches. For instance, you might use heatmap data to identify a page with a high drop-off rate (the "what"), and then conduct moderated usability tests to understand the user frustration causing it (the "why"). This synergy transforms data points into actionable narratives.
Ultimately, mastering these user testing methods is about more than just fixing usability issues. It's about building a culture of user-centricity where every decision is informed by genuine user understanding. This commitment minimizes risk, saves development costs, and is the most reliable path to creating products that people not only use but truly love. The insights are waiting for you; now you have the tools to go and find them.
Ready to streamline your feedback process and turn insights into action faster? Beep integrates seamlessly into your workflow, allowing you to capture contextual feedback with screenshots and annotations directly on your site or app. Stop juggling spreadsheets and start collaborating visually. Try Beep today to accelerate your user testing cycle.

.png)
Comments